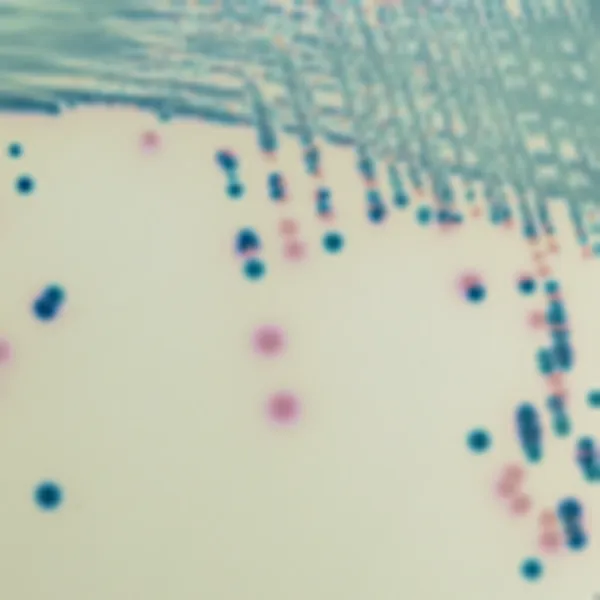
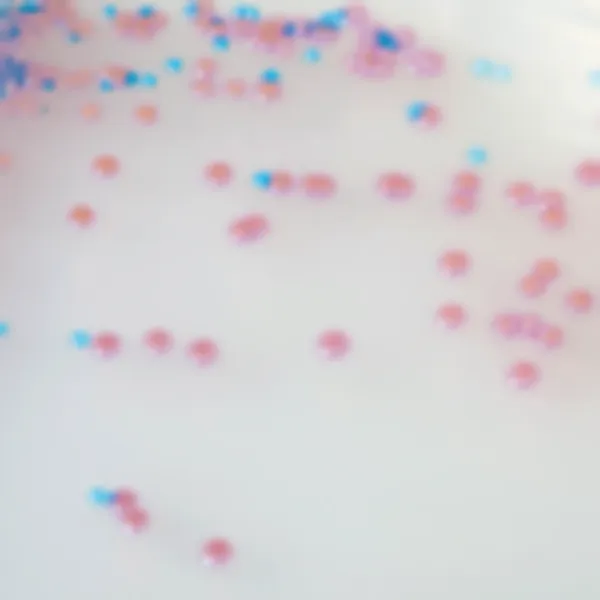
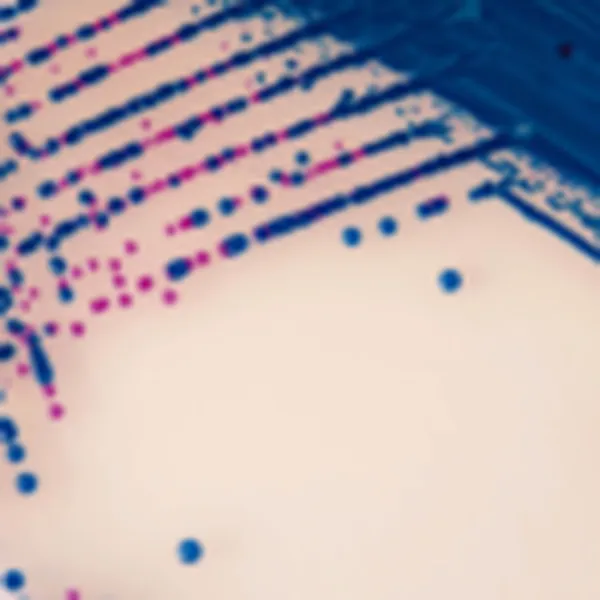
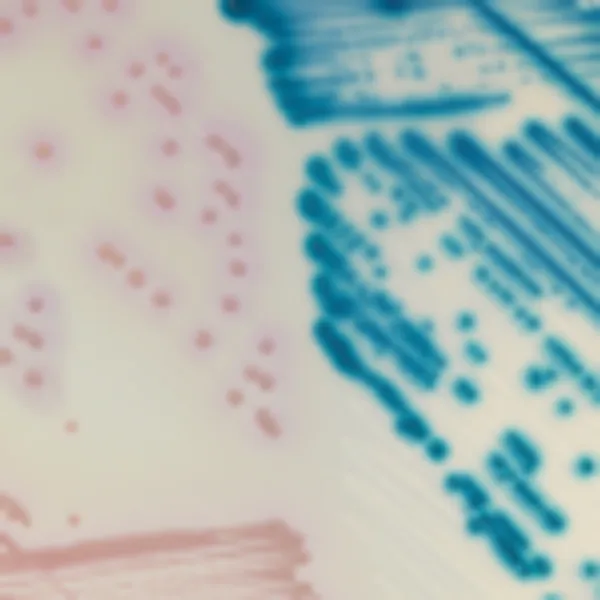
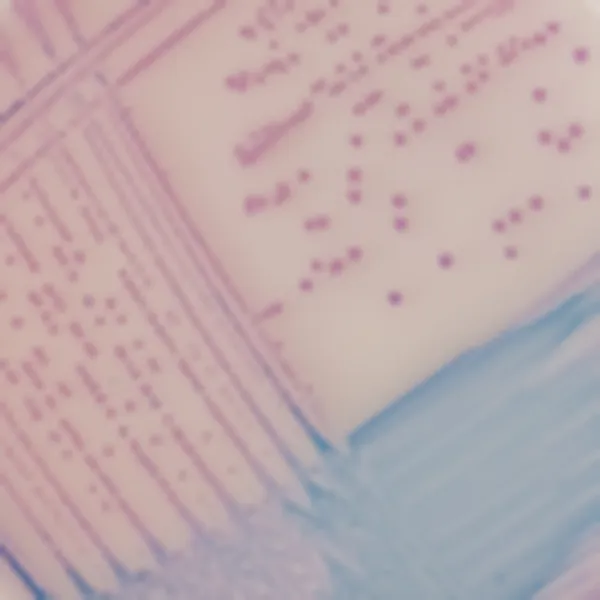
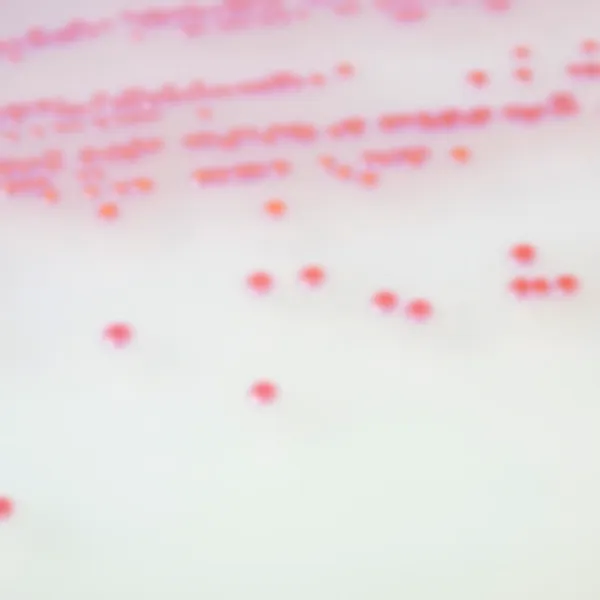
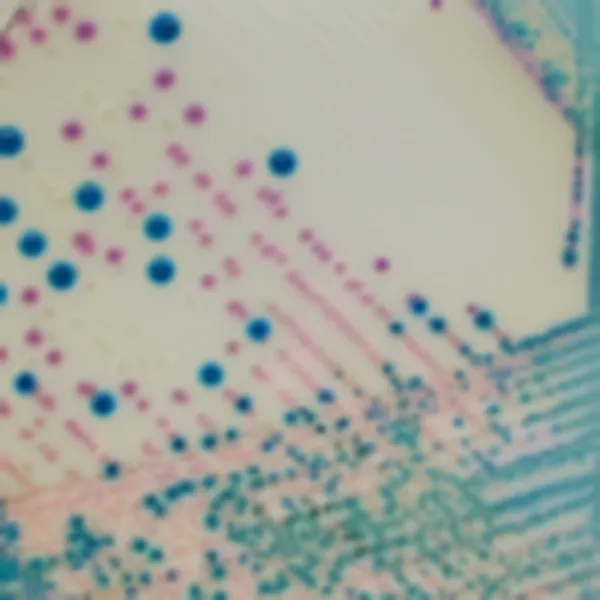
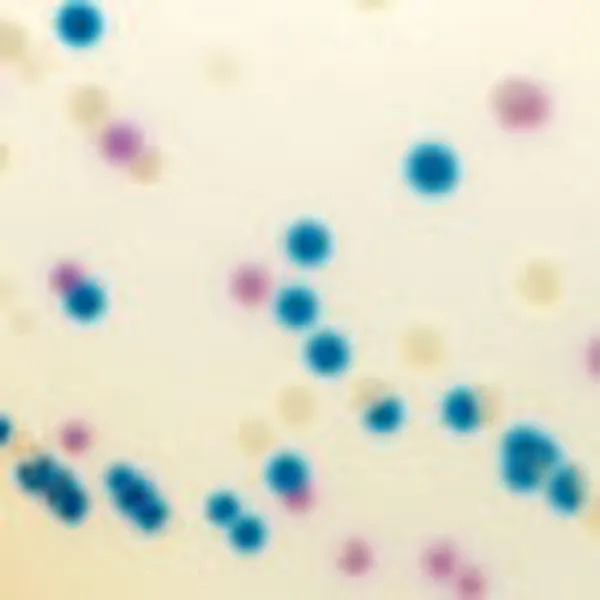
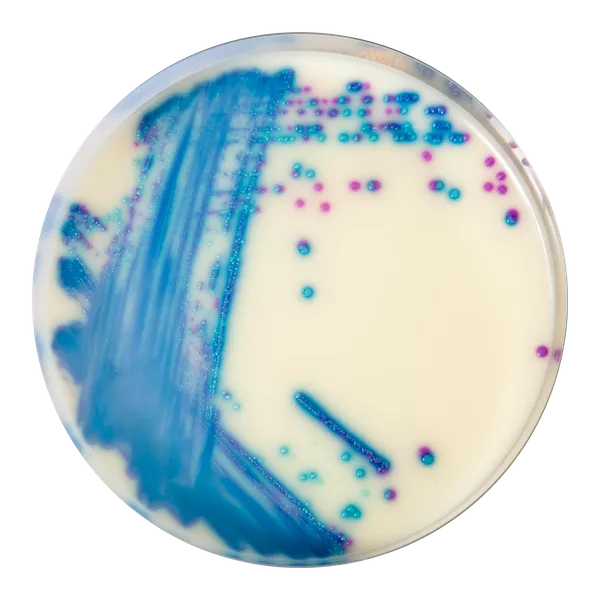
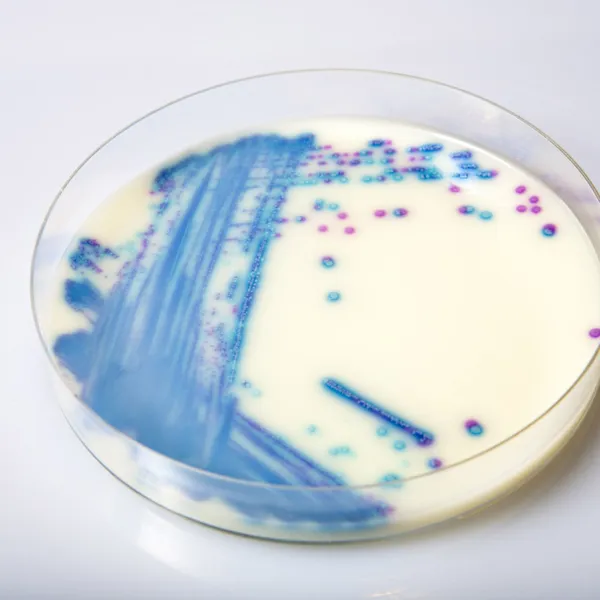
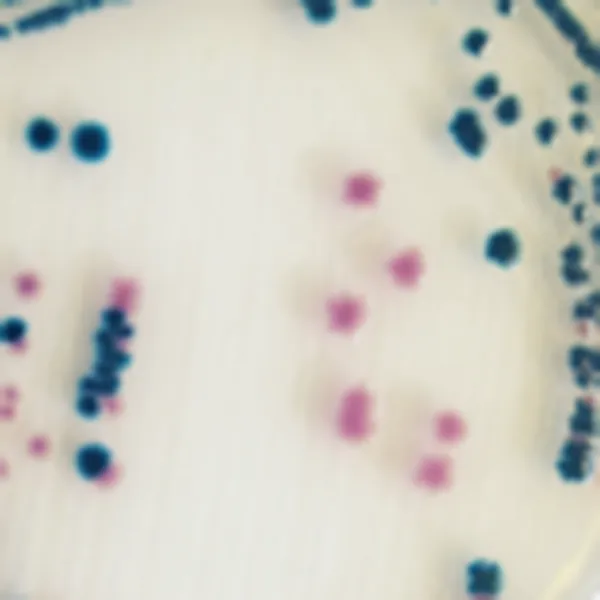
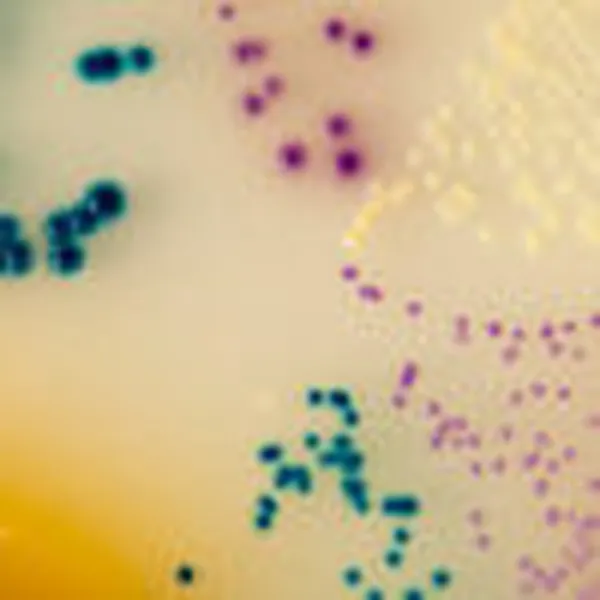
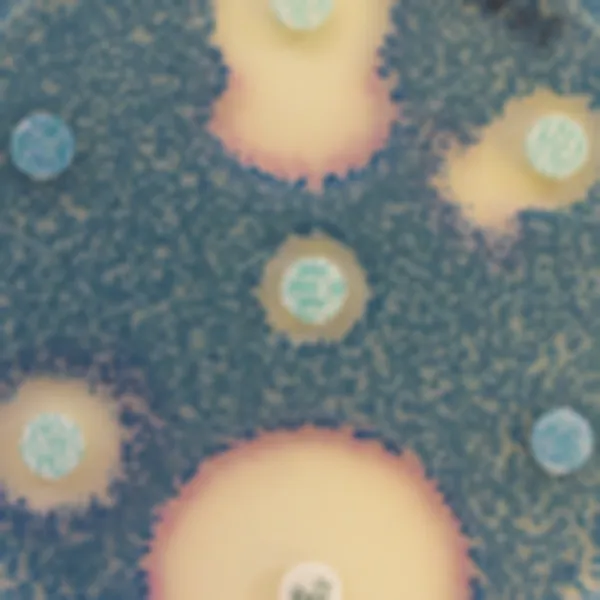
Colonies Appearance

ERV. faecalis/ERV. faecium
Pink to mauve

E. gallinarum/E. casseliflavus
Blue or inhibited
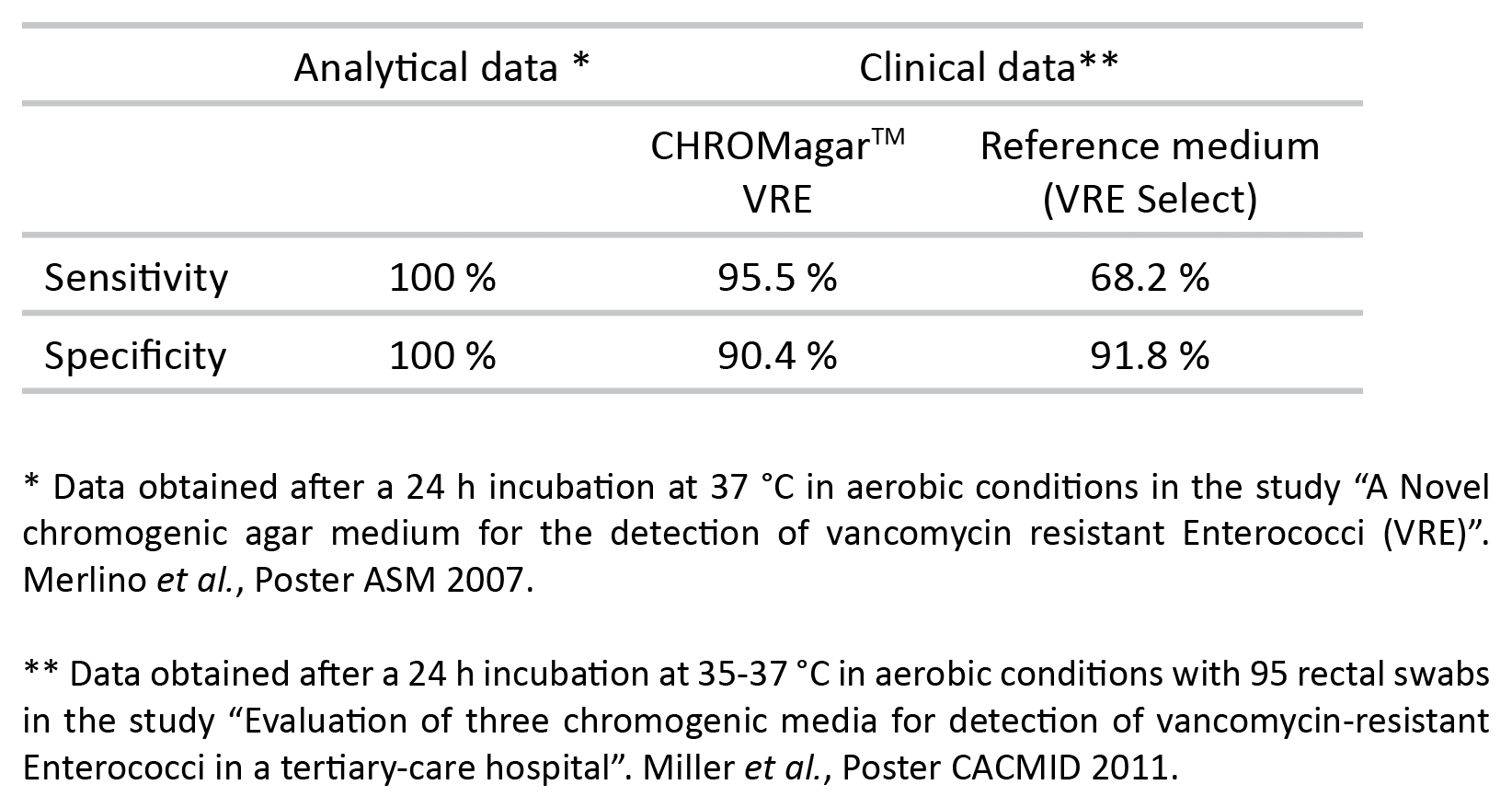
Performance
Performance
There are two types of vancomycin resistance in Enterococci. The first type is intrinsic resistance (mostly Van C type but also Van D, Van E, Van F etc) found in E. gallinarum and E. casseliflavus/E. flavescens and demonstrates a low-level resistance to vancomycin. The second type of vancomycin resistance in enterococci is acquired resistance (Van A & Van B types), mostly seen in E. faecium and E. faecalis. Therefore, to avoid the spread of this resistance to more virulent pathogens (S. aureus, for instance) it is crucial to promptly detect the presence of any of these two species in the patient, and accurately differentiate them from other Enterococci.
“Knowledge of the type of resistance is critical for infection control purposes. Van A and Van B genes are transferable and can spread from organism to organism. In contrast, Van C genes are not transferable, have been associated less commonly with serious infections, and have not been associated with outbreaks” – from CDC guidelines
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) infections are especially aggressive and have been associated with mortality rates approaching 60 % to 70 %.
Intended Use :
CHROMagar™ VRE is a selective and differential chromogenic medium, containing 6 mg/L of vancomycin, intended for use in the qualitative direct detection of vanA/vanB transmissible VRE-type gastrointestinal colonization with vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis (VRE) to aid in the prevention and control of VRE in healthcare settings. The test is performed with rectal swab and stools from patients to screen for VRE colonization. Results can be interpreted after 24 h of aerobic incubation at 35-37 °C.
The medium can also be used as an early warning indicator for diagnostic tests of infections to signal the possible presence of multi drug-resistant bacteria. This use does not replace the institution’s protocols. CHROMagar™ VRE is not intended to diagnose VRE infection nor to guide nor monitor treatment for infections. A lack of growth or the absence of pink colonies on CHROMagar™ VRE does not preclude the presence of VRE. Further identification, susceptibility testing, and epidemiological typing is needed on suspect colonies.
1. Simple, fast and reliable tool : for the direct detection of VRE strains with transmissible resistance : this is a precious help in the implementation of the appropriate control measures to prevent the spread of VRE.
2. Intense colonie colours: In CHROMagar™ VRE, VRE. faecalis et VRE. faecium strains are easily distinguishable by the colony colour. In the contrary, in the classical agar for the detection of VRE (Bile Esculine Agar supplemented with vancomycin) :
(I) there is no différenciation between E. faecalis/ E. faecium ; (II) it often leads to false positives of other esculine hydrolising bacteria (like Lastococcus, Pediococcus...) ; (III) the black "cloud" makes plate reading difficult as well as the choice of the proper colony for further confirmatory tests.
3. Flexibility : CHROMagar™ VRE is supplied with a more than 18 months shelf life. This allows for flexibility of use, whether in an epidemic situation with many patients to screen, or whether for random surveillance of cultures.
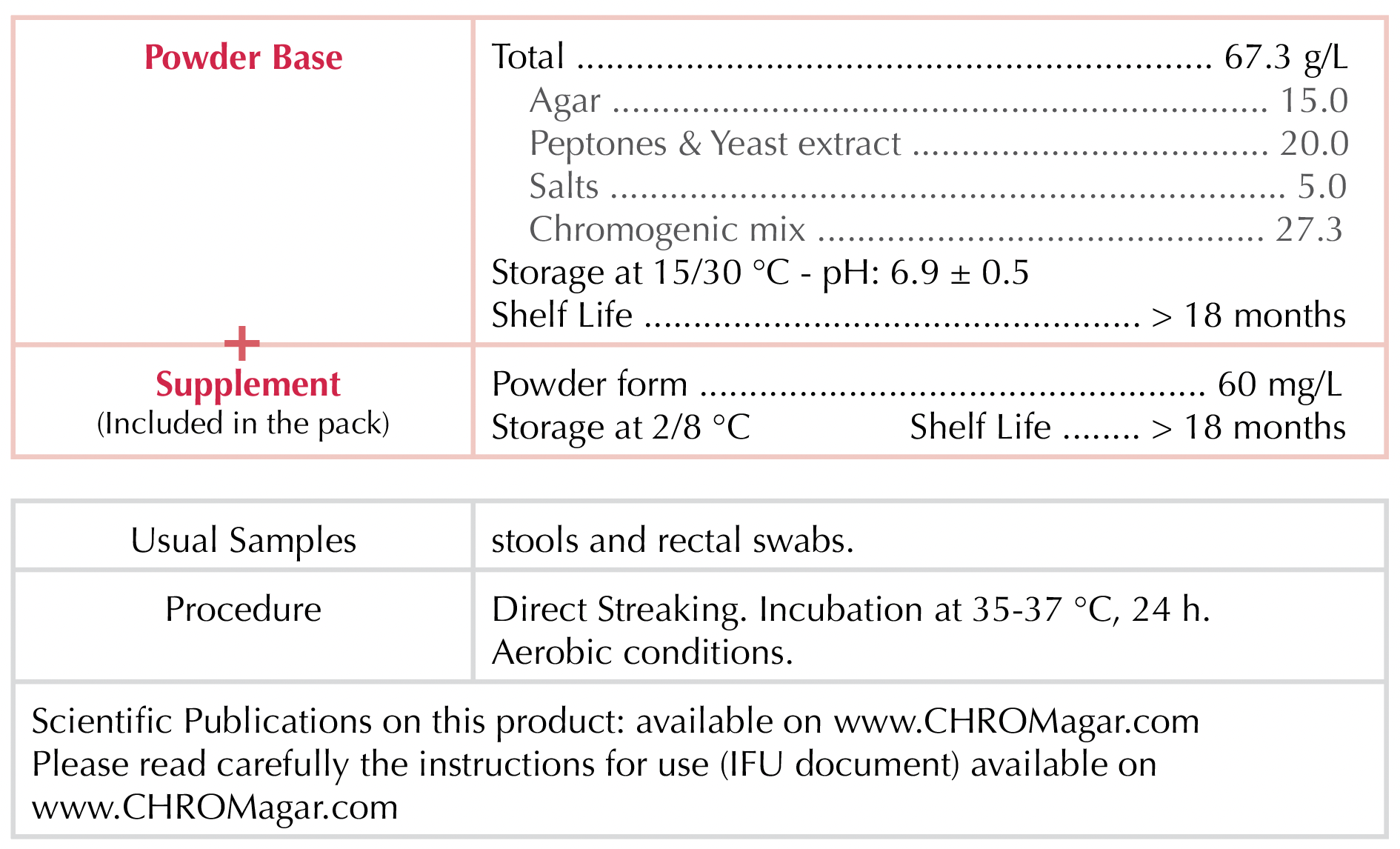
Composition
Technical Documents
Scientific Publications
2023
Comparison of Five Different Selective Agar for the Detection of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus faecium
📄 Publication2013
Performance of CHROMagar VRE medium for the detection of Airborne Vancomycin-resistant/sensitive Enterococcus species
📄 Publication2012
Evaluation of CHROMagar compared with enterococcosel broth for the isolation of vancomycin resistant enterococci
📄 Publication2012
A novel method “CHROMagar” for screening vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) isolates
📄 Publication2011
Evaluation of Three Chromogenic Media for Detection of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci in a tertiary-care Hospital M.L. Miller et al.
📄 Publication2011
Evaluation of Three Commercial Chromogenic Media and BEAA + van 6ug/mL for the Detection of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus (VRE)
📄 Publication2011
Evaluation of Broth Enrichment for the Detection of Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci on Two Chromogenic Media
📄 Publication2009
Evaluation of a ColorexTM chromogenic media and Bile-esculin azide agar with 6ug vancomycin for the detection of Vancomycin Resistant Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium (VRE)
📄 Publication2009
Evaluation of Chromogenic Agar for Screening Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE)
📄 Publication2009
Comparison of two chromogenic media for selective isolation of vancomycin-resistant enterococci from stool specimens
📄 Publication2008
Evaluation of Two Chromogenic Media for the Isolation of VRE (Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci)
📄 Publication2008
Evalucion de un Medio Cromogénico (CHROMagar) Para La Detection de Enterococos Resistentes a Vancominica (EVR) a partir de Hisopados Rectales
📄 Publication2007
A novel Chromogenic Agar Medium for the Detection of Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci (VRE)
📄 Publication2020
A genomic epidemiology study of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Acinetobacter baumannii in two intensive care units in Hanoi, Vietnam
📄 Publication
















Read more