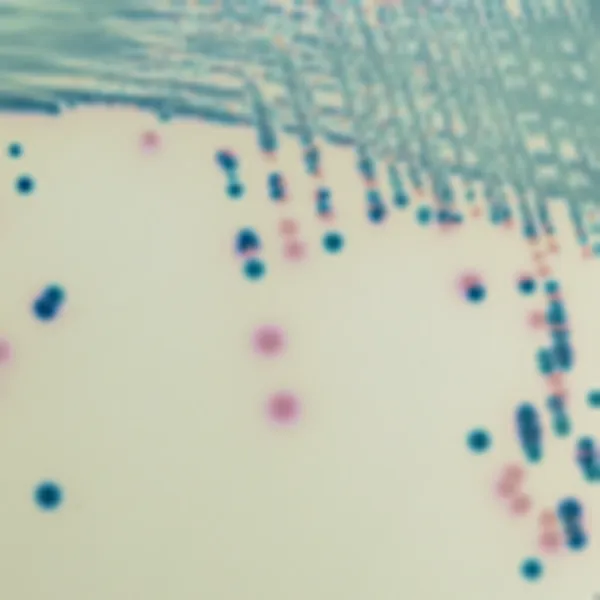
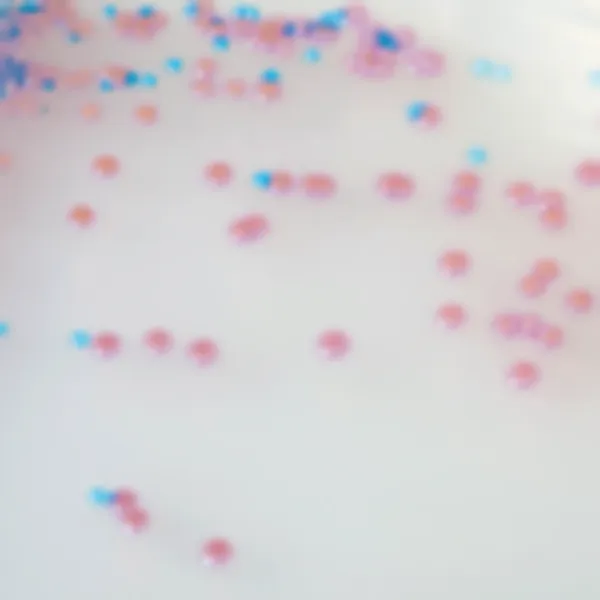
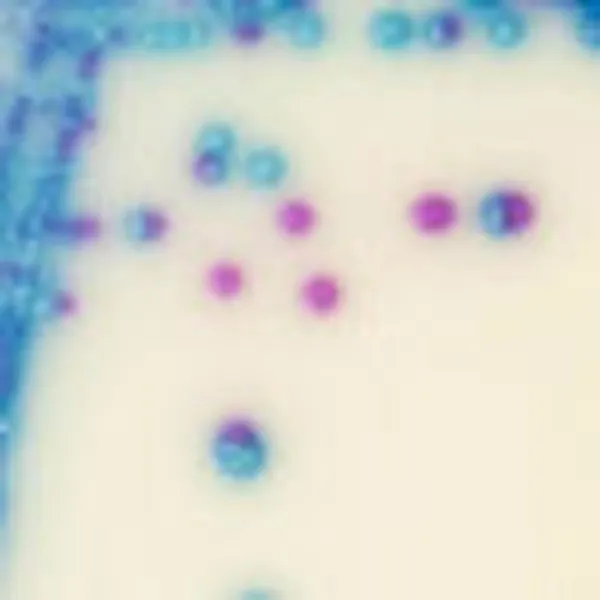
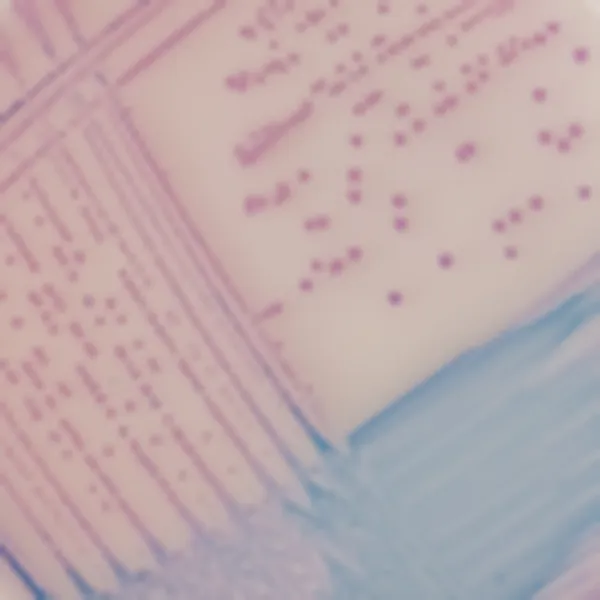
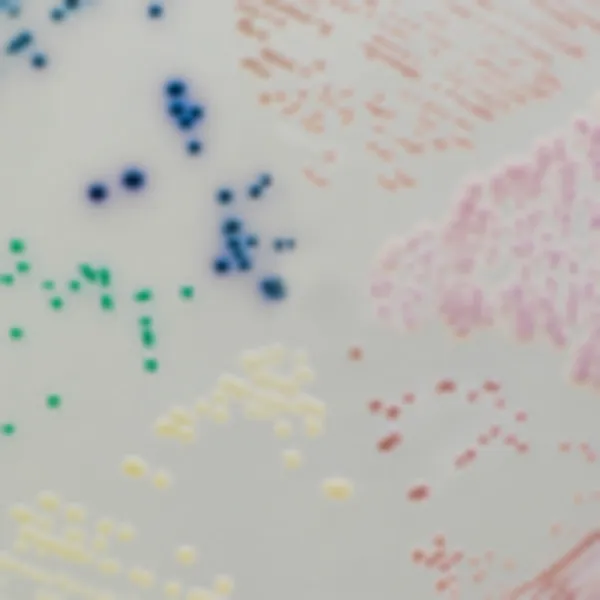
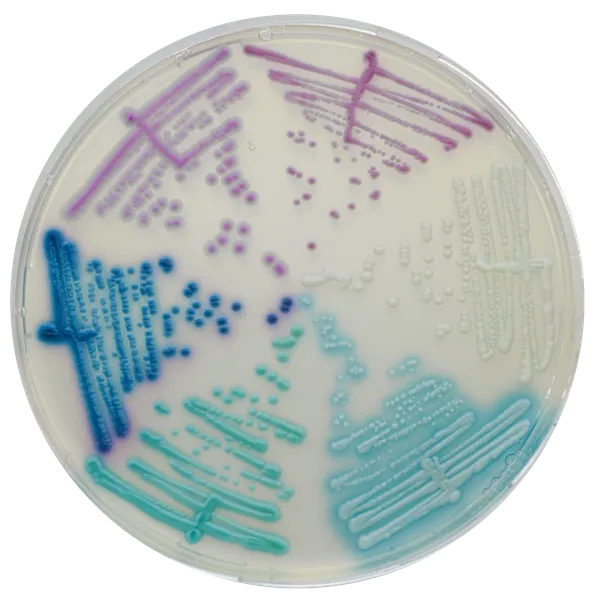
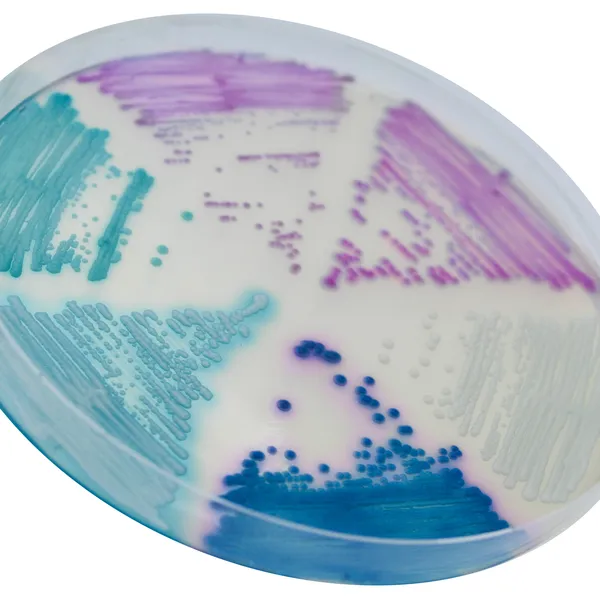
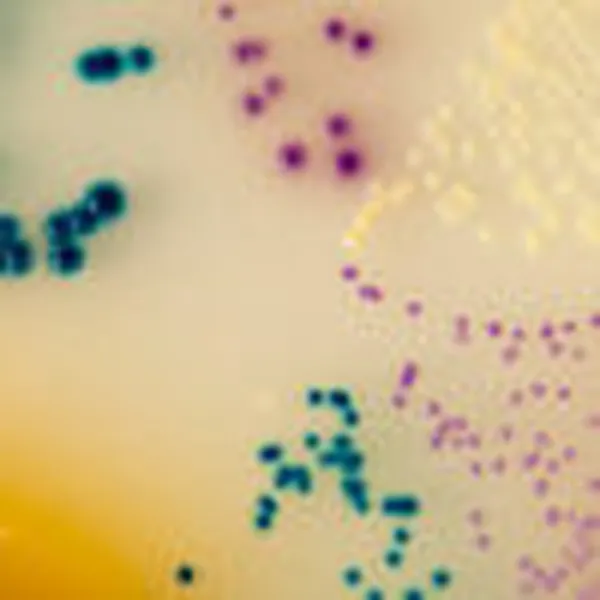
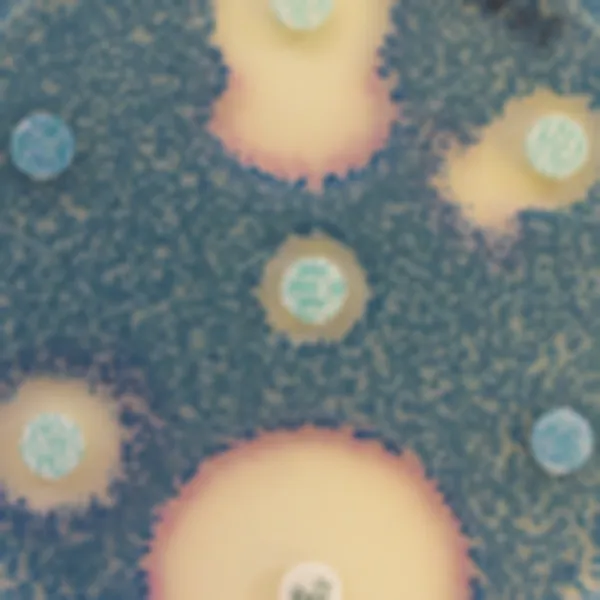
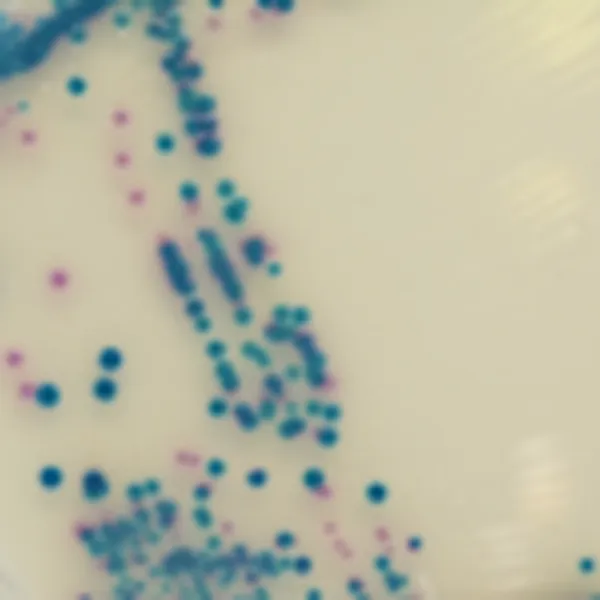
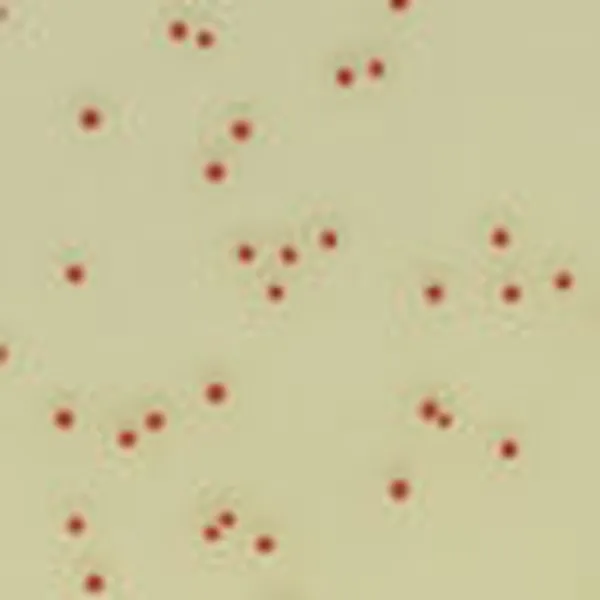
Colonies Appearance

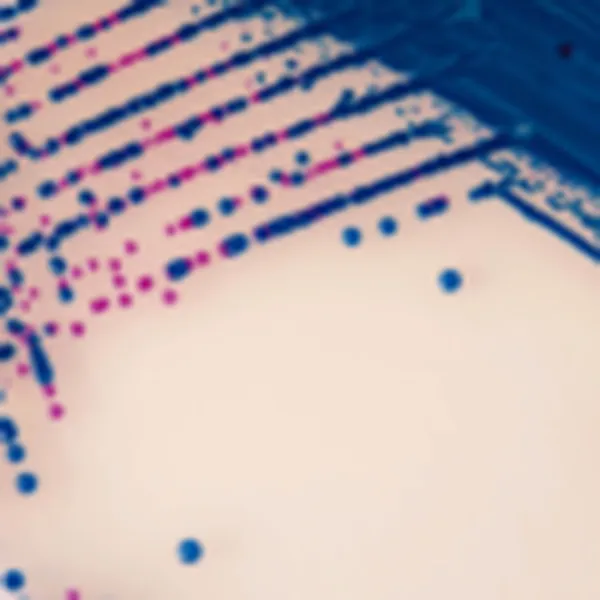
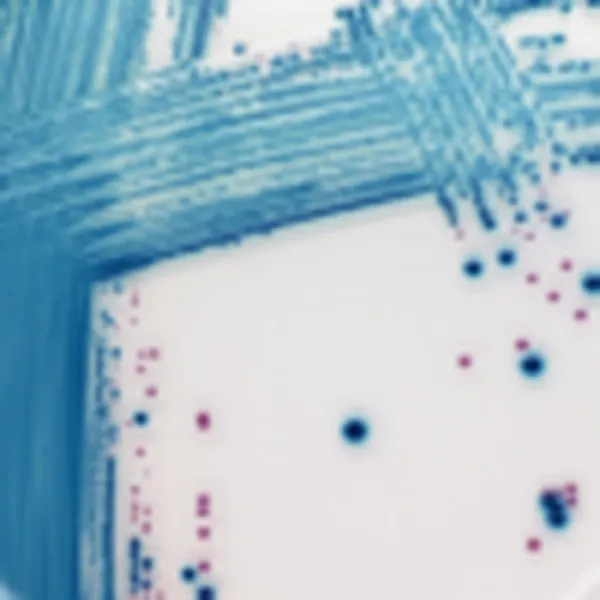
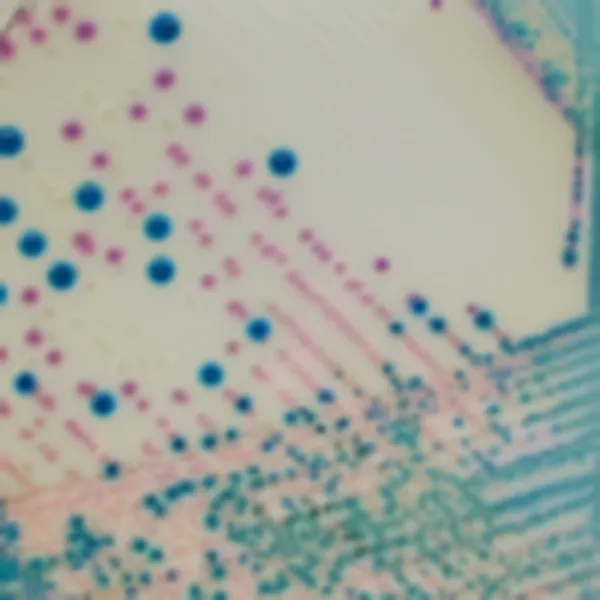
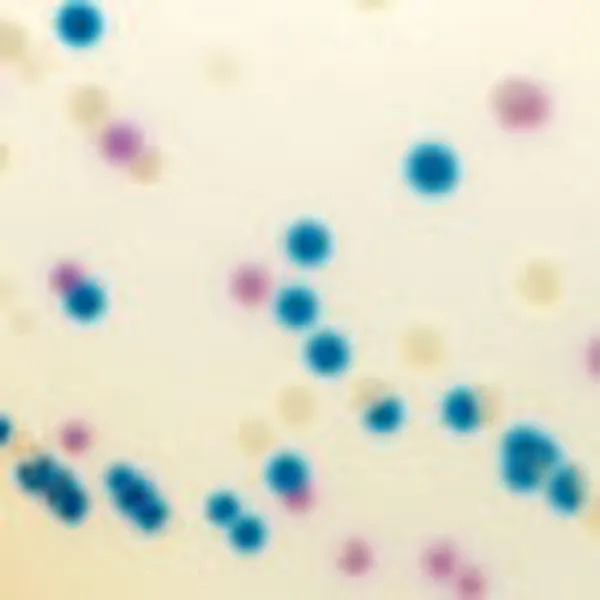
C. auris (Front)
Light blue with blue halo

C. auris (Back)
Light blue with blue halo

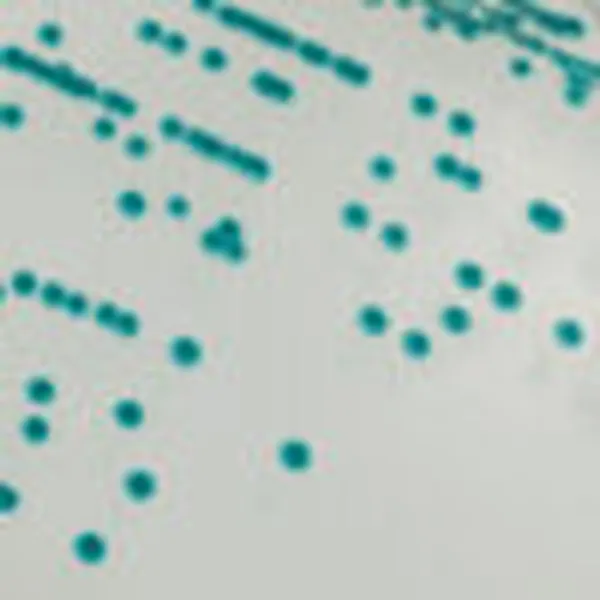
C. albicans
Green-blue

C. tropicalis
Metallic blue with pink halo

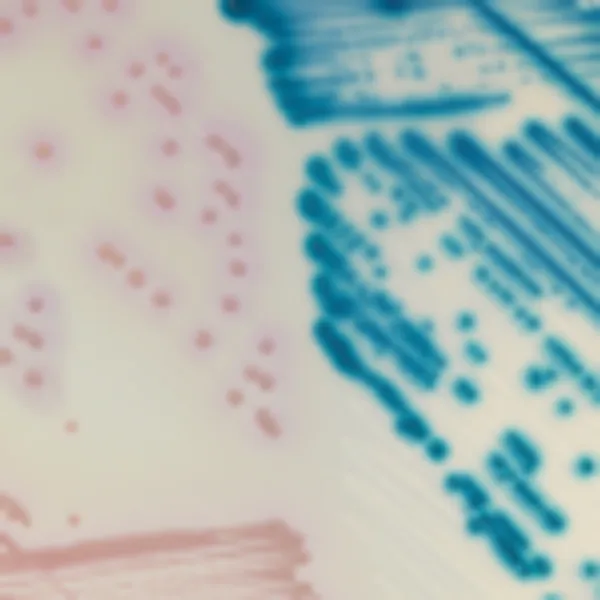
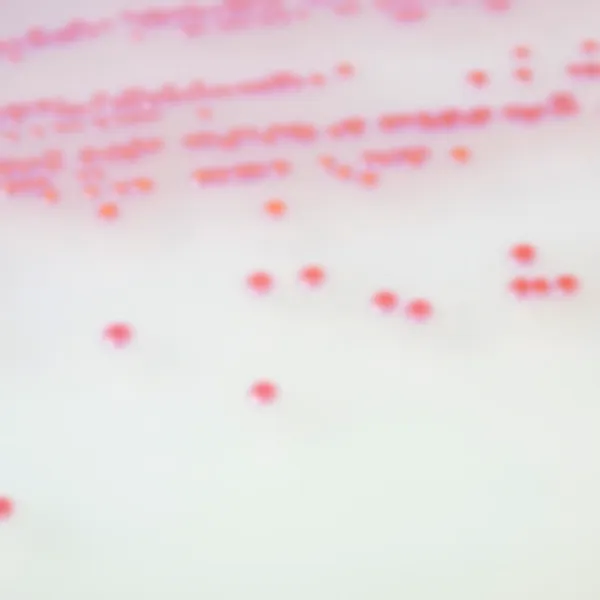
C. krusei
Pink and fuzzy

C. glabrata
Mauve
Performance
Performance
Candida are yeast species involved in various infections called candidiasis, which can affect damaged skin, respiratory tract, digestive and urogenital systems. These candidiasis can be severe with significant morbidity for nosocomial infections or in immunocompromised patients. Although C. albicans is still the main species involved, the use of antifungal agents has given rise to other species such as C. tropicalis, C. krusei and C. glabrata.
In 2016, the World Health Organization added C. auris to this list, with a prevalence of over 90 % resistant to fluconazole. In addition, some strains are multidrug resistant to amphotericin B, voriconazole, and/or echinocandins.
CHROMagar™ Candida Plus is the first chromogenic isolation medium to detect and differentiate C. auris in addition to other major clinical Candida species such as C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. glabrata or C. krusei.
Intended Use :
CHROMagar™ Candida Plus is a selective chromogenic culture medium intended for use in the qualitative direct detection, differentiation and presumptive identification of Candida species including C. auris. The test is performed with swabs from skin, throat, ears and vaginal specimens as well as sputum, urine and stools samples, in parallel to cultures on Sabouraud agar, to aid in the Candidiasis diagnosis. Results can be interpreted after 24-48 h of aerobic incubation at 30-37 °C.
Further microbiological testing or epidemiological typing are needed. A lack of growth or the absence of colonies on CHROMagar™ Candida Plus does not preclude the presence of Candida. CHROMagar™ Candida Plus is not intended to diagnose infection nor to guide nor monitor treatment for infections.
1. High Specificity : Differentiation of the most common Candida species with very high specificity (analytical data) :
- C. albicans 100 %*
- C. tropicalis 100 %*
- C. krusei 100 %*
* Data obtained after a 48 h incubation at 37 °C in aerobic conditions in the study « Evaluation of a novel chromogenic medium for Candida spp. identification and comparison with CHROMagar™ Candida for the detection of Candida auris in surveillance samples. Mulet Bayona et al., 2020. Diag. Microbiol. Inf. Dis.
2. Unique medium to differentiation C. auris from other Candida species owe to high specificity, it can be used also as a screening tool in case of outbreaks for patient samples and surfaces suspecyted of being contaminated with C. auris.
For C. auris :
- Specificity 100 %*
- Sensitivity 100 %*
** Data obtained after a 24-48 h incubation at 37 °C in aerobic conditions with 364 patients surveillance samples and 212 environmental samples in the study «Novel chromogenic medium CHROMagar™ Candida Plus for detection of Candida auris and other Candida species from surveillance and environmental samples: A multicenter study. Mulet Bayona et al., 2022. J. of Fungi.
3. Easy identification: Identification by MALDI-TOF can be carried directly from a colony. No need of subculture.
Composition
 <img class="vce-single-image" src="/Composition-EN-7-1756442697.png" width="670" height="350" alt="" title="Composition EN" />
<img class="vce-single-image" src="/Composition-EN-7-1756442697.png" width="670" height="350" alt="" title="Composition EN" /> Technical Documents
Scientific Publications
2025
Keep the Hospital Clean: Diagnostic Performance of Ten Different Molecular and Culture‑Based Methods to Detect Candidozyma (Candida) auris
📄 Publication2024
Verification, Analytical Sensitivity, Cost-effectiveness, and Comparison of four Candida auris Screening Methods
📄 Publication2023
A Novel One Health Approach concerning Yeast Present in the Oral Microbiome of the Endangered Rio Skate (Rioraja agassizii) from Southeastern Brazil
📄 Publication2023
Evaluation of the CHROMagar Candida Plus mediumfor presumptive identification of yeasts and MALDI-TOF MS identification
📄 Publication2023
A case of fungal otitis externa caused by coinfection of Candida auris and Aspergillus flavus
📄 Publication2023
Accuracy of the WASPLab PhenoMATRIX Algorithm for the Identification of Candida auris on Candida Plus CHROMagar Colorex
📄 Publication2023
Colonized patients by Candida auris: Third and largest outbreak in Brazil and impact of biofilm formation
📄 Publication2023
Utility of CHROMagarTM Candida Plus for presumptive identification of Candida auris from surveillance samples
📄 Publication2023
A case of fungal otitis externa caused by coinfection of Candida auris and Aspergillus flavus
📄 Publication2022
Evaluation of CHROMagar Candida Plus for presumptive identification of Candida auris
📄 Publication2022
Comparison of Candida colonization in intensive care unit patients with and without Covid-19: first prospective cohort study from Turkey
📄 Publication2022
Evaluation of a new chromogenic agar for identification of Candida species including Candida auris
📄 Publication2022
Evaluation and Validation of Optimal Laboratory screening methods using a custom dulcitol agar and commercially available chromogenic agars in detecting Candida auris growth
📄 Publication2022
Assesing the limit of detection of Candida auris screening methods using direct-to-agar, broth-enriched-culture, direct-polymerase chain reaction, and broth-enriched-polymerase chain reaction
📄 Publication2022
Successful control of Candida auris transmission in a German COVID-19 intensive care unit
📄 Publication2022
Novel Chromogenic medium CHROMagar Candida Plus for detection of Candida auris and other Candida species from surveillance and environmental samples: a multi center study
📄 Publication2021
The performance of two novel chromogenic media for the identification of multi-drug resistant Candida auris compared with other commercially available formulations
📄 Publication2020
Evaluation of a novel chromogenic medium for Candida spp. identification and comparison with CHROMagar Candida for the detection of Candida auris in surveillance samples
📄 Publication2020
CHROMagar Candida Plus: A novel chromogenic agar that permits the rapid identification of Candida auris
📄 Publication

















Read more