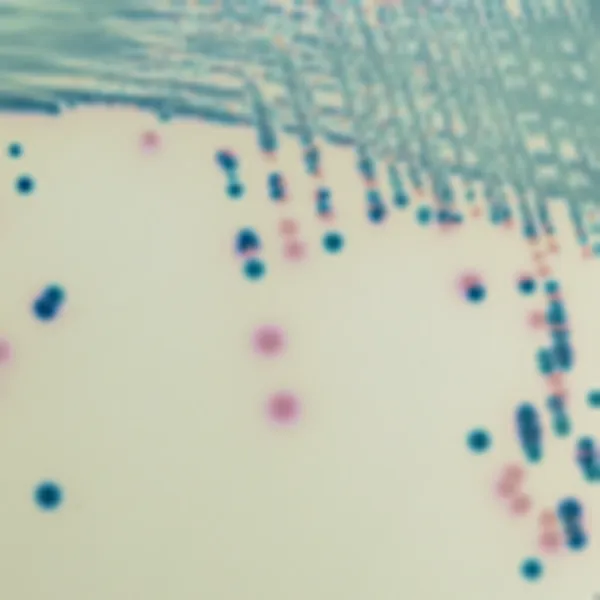
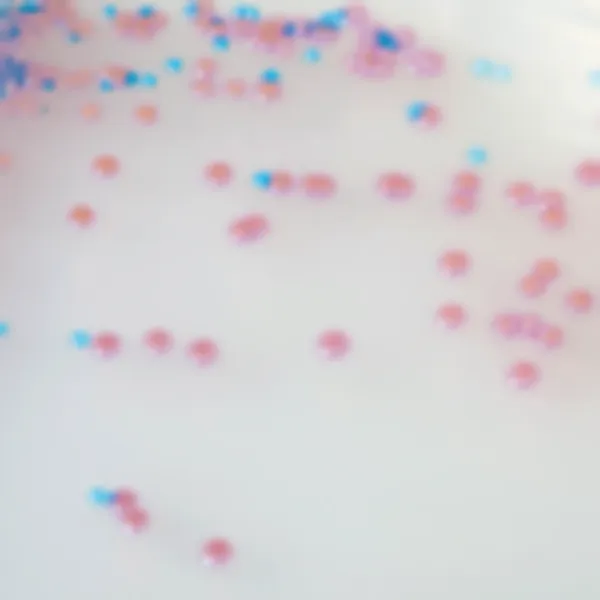
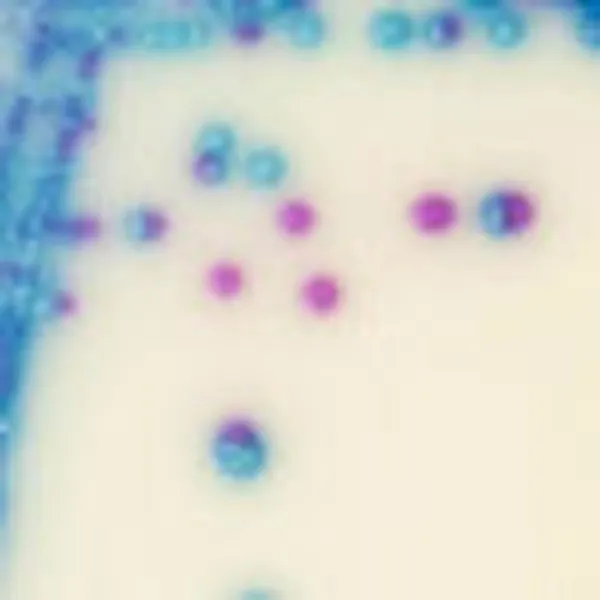
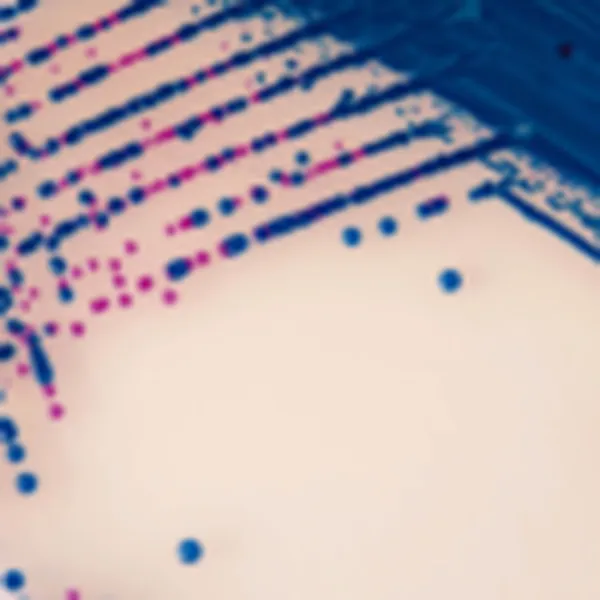
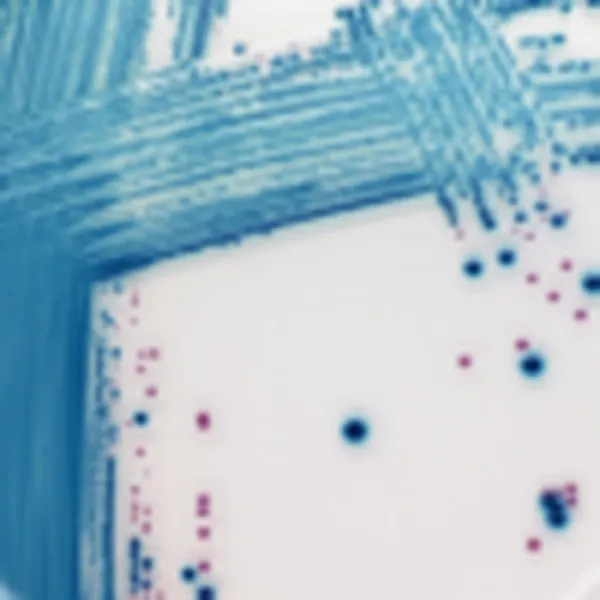
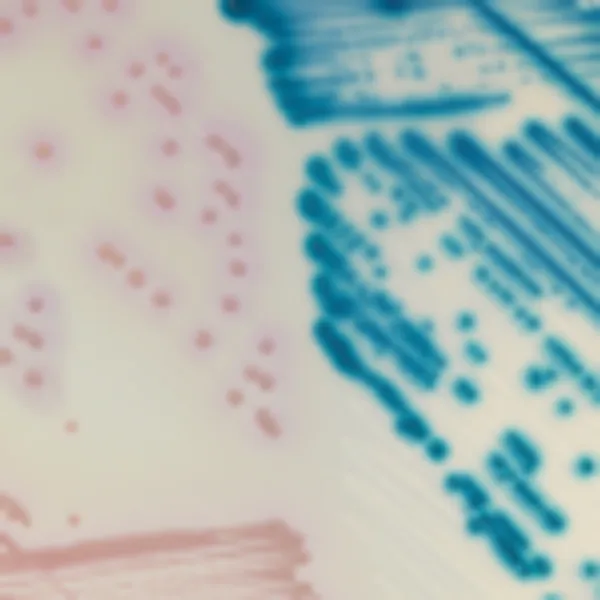
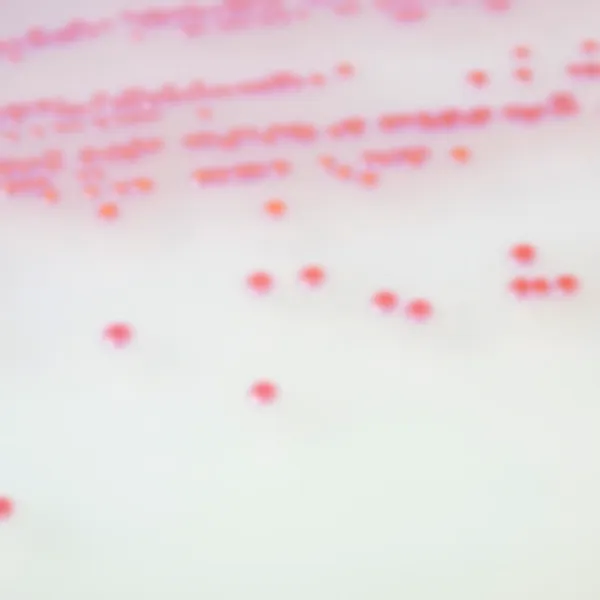
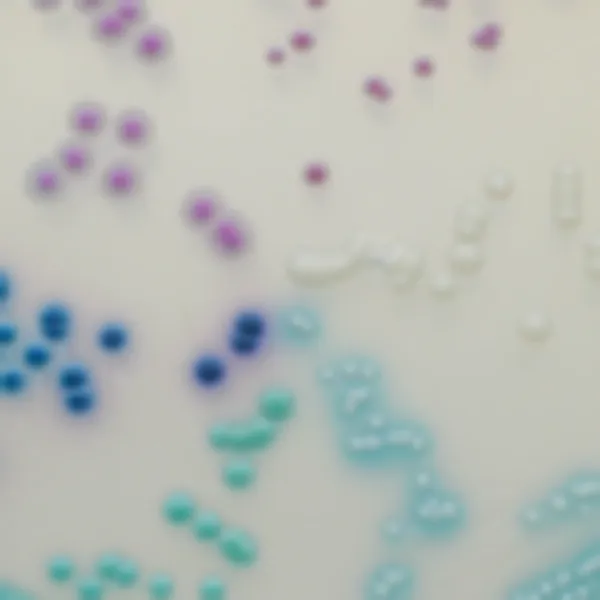
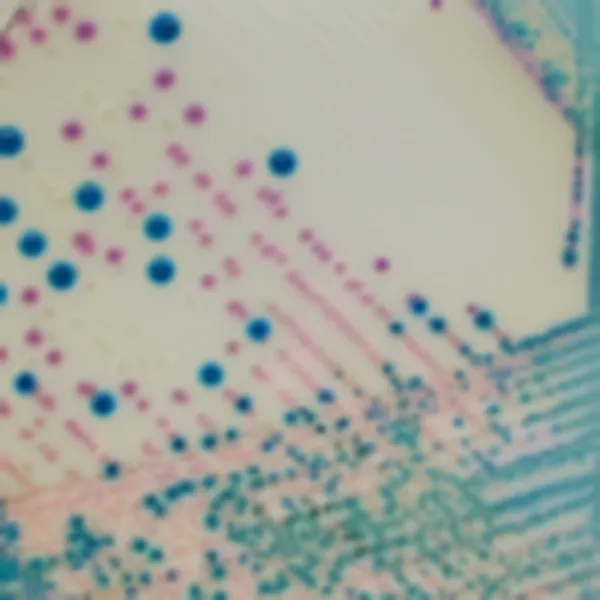
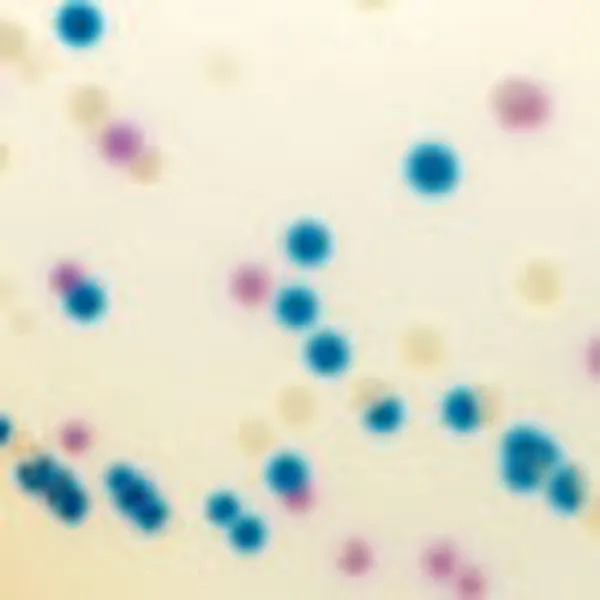
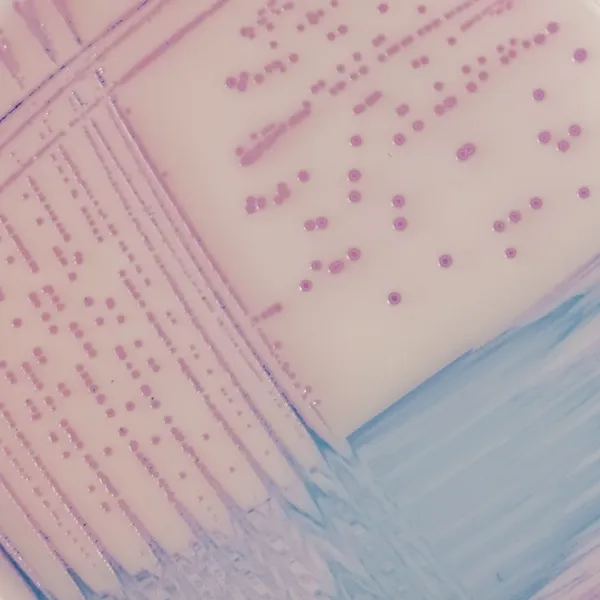
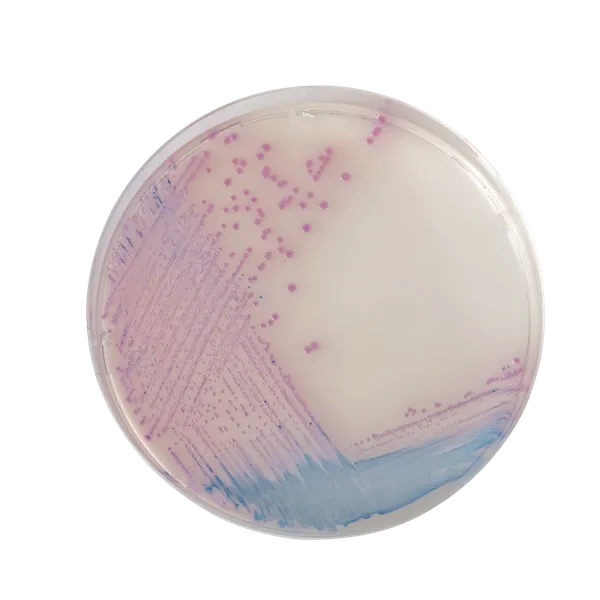
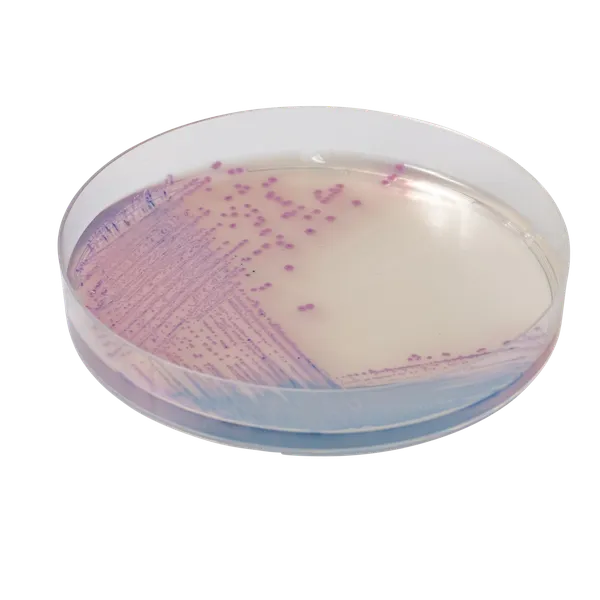
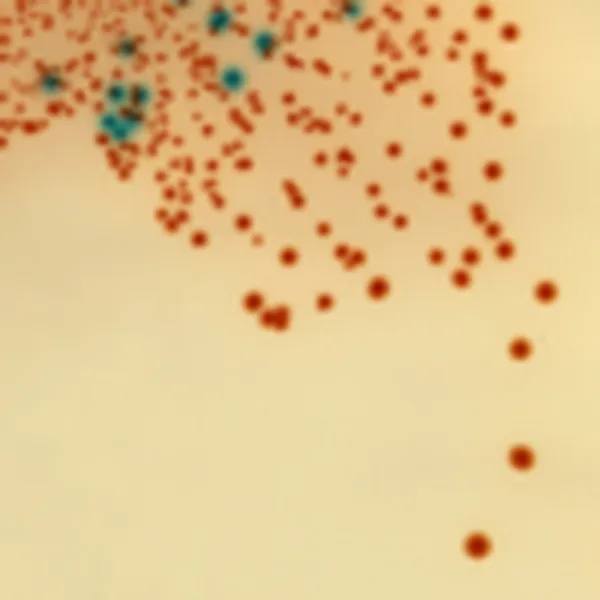
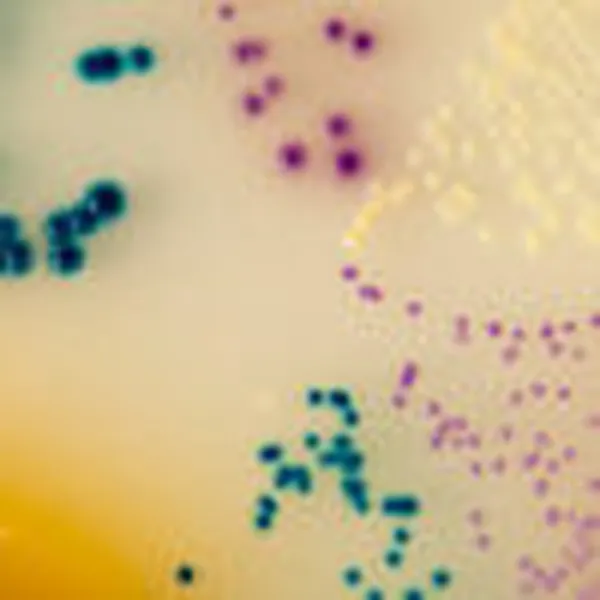
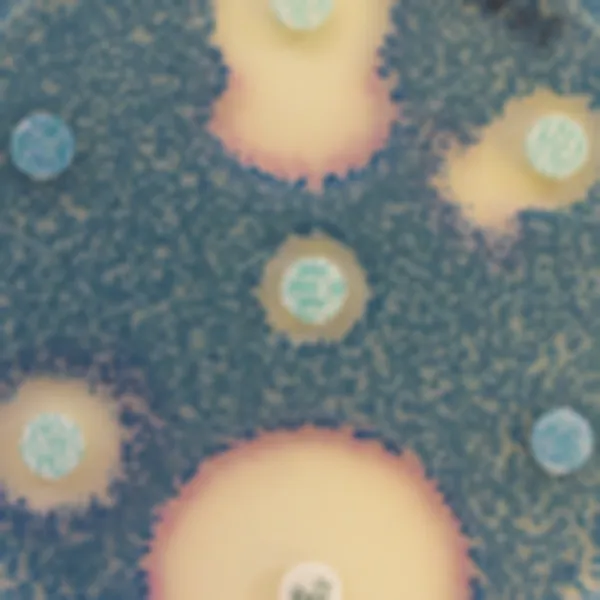
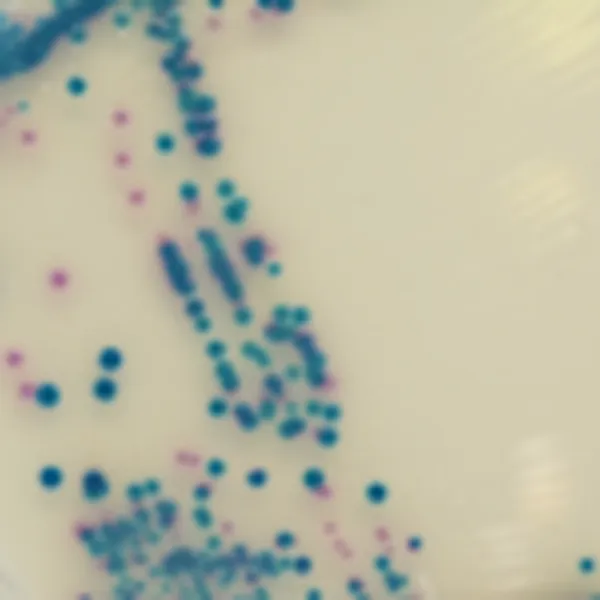
Colonies Appearance

Salmonella including S. Typhi
Mauve

Other bacteria
Blue, colourless or inhibited
Performance
Performance
Infections caused by Salmonella spp, including Salmonella Typhi, remain a major worldwide health problem:
• In the US, Salmonella has an incidence rate of 16.47 cases per 100,000 (CDC estimation, 2010).
• In Europe, it is reported as the first bacterial cause of food outbreaks (EFSA/ECDC 2011 report, 2009 figures)
• In developing countries, Salmonella Typhi and Paratyphi are commonly encountered with an estimated annual incidence of about 17 million cases. (2007 EFSA report)
Moreover, according to a recent WHO report, Salmonella infections are responsible for 2 million deaths per year from diarrhoea. Salmonella is the second most reported zoonotic infection in humans (EFSA/ECDC 2011 report, 2009 figures).
Mainly due to contamination in the food chain and/or during food-production processes, Salmonella commonly induces enteric illness whose major symptoms are abdominal cramps, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting. More severe cases, for instance typhoid cases or infections
Intended Use :
CHROMagar™ Salmonella is a selective chromogenic culture medium intended for use in the qualitative direct detection, differentiation, and presumptive identification of Salmonella. The test is performed with rectal swabs and stools, to aid in the diagnosis of Salmonella infections. Results can be interpreted after 18-24 h of aerobic incubation at 35-37 °C.
Concomitant cultures are necessary to recover organisms for further microbiological testing or epidemiological typing. A lack of growth or the absence of mauve colonies on CHROMagar™ Salmonella does not preclude the presence of Salmonella.
CHROMagar™ Salmonella is not intended to diagnose infection nor to guide nor monitor treatment for infections.
CHROMagar™ Salmonella can also be used in the detection of Salmonella in the analyses of food products for human consumption, animal feed and in environmental samples.
1. Easy reading : Intense mauve colony colours for better identification and partial inhibition of E. coli and coliforms.
2. Greater specificity / less workload : Conventional media for the detection of Salmonella by H2S character have very poor specificity resulting in numerous false positives. (Citrobacter, Proteus, etc.) among the rare, real positive Salmonella. The workload for unnecessary examination of suspect colonies is so heavy that real positive Salmonella colonies might often be overlooked in routine testing.
Because of their poor specificity, conventional media require a tedious examination of at least 10 colonies per suspected sample. On the contrary, CHROMagar™ Salmonella eliminates most of those false positives and allows technicians to focus on the real contaminated samples.
3. High Sensitivity and Specificity leading to a higher detection rate of Salmonella
Analytical Data
- Sensitivity : (81 %) and 93 % *
- Specificity : 100 %
Clinical Data
- Sensitivity : 95 %*
- Specificity : 88,9 %* compared to 78,5 % with Hektoen Agar
* In-house data obtained after a 24-48 h incubation at 37 °C in aerobic conditions. Sensitivity % in parenthesis includes lactose positive Salmonella species growing in blue. 2012.
** Data obtained after a 18-24 h incubation at 37 °C in aerobic conditions with 508 stool samples analyzed in the study “Comparison of CHROMagar™ Salmonella medium and Hektoen Enteric Agar for isolation of Salmonellae from stool samples“. Gaillot et al., 1998. J. Clin. Microbiol.
4. Dramatic reduction of the workload : Number of useless confirmatory tests is minimized since there is no need of duplicating them.
Composition

Technical Documents
Scientific Publications
2004
Development of a novel cross-streaking method for isolation, confirmation, and enumeration of Salmonella from irrigation ponds
📄 Publication2003
Comparison of four chromogenic media and Hektoen Agar for detection and presumptive identification of Salmonella strains in human stools
📄 Publication2002
Comparison of CHROMagar Salmonella medium and Xylose-Lysine-Desoxycholate and Salmonella-Shigella Agars for isolation of Salmonellae from stool samples.
📄 Publication1999
Comparison of CHROMagar Salmonella medium and Hektoen Enteric Agar for isolation of Salmonellae from stool samples
📄 Publication2011
Rapid detection of Salmonella in Chicken meat using immunomagnetic separation, CHROMagar, Elisa and Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
📄 Publication2006
Salmonella Prevalence and Total Microbial and Spore Populations in Spices Imported to Japan
📄 Publication2005
Evaluation of three enrichment broths and five plating media for Salmonella detection in poultry
📄 Publication
















Read more