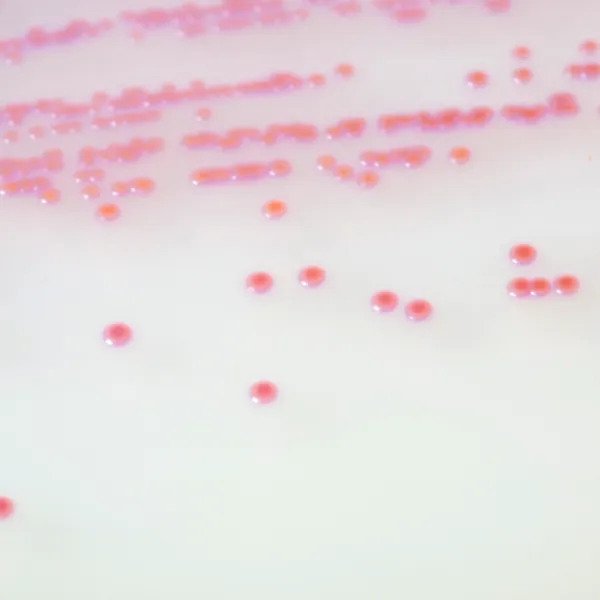
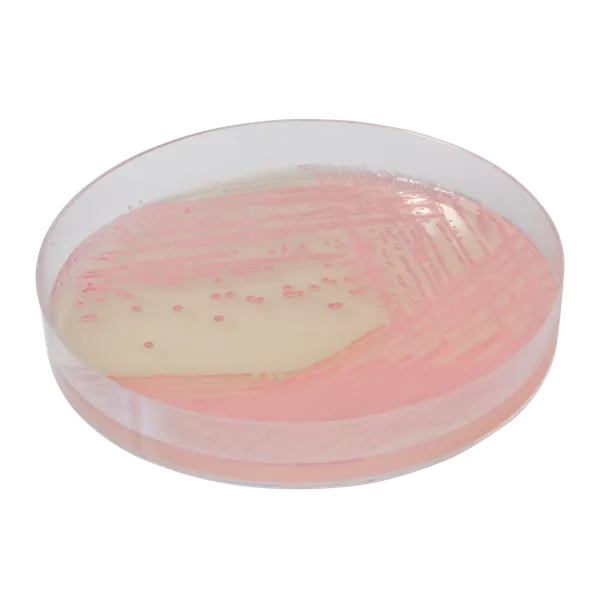
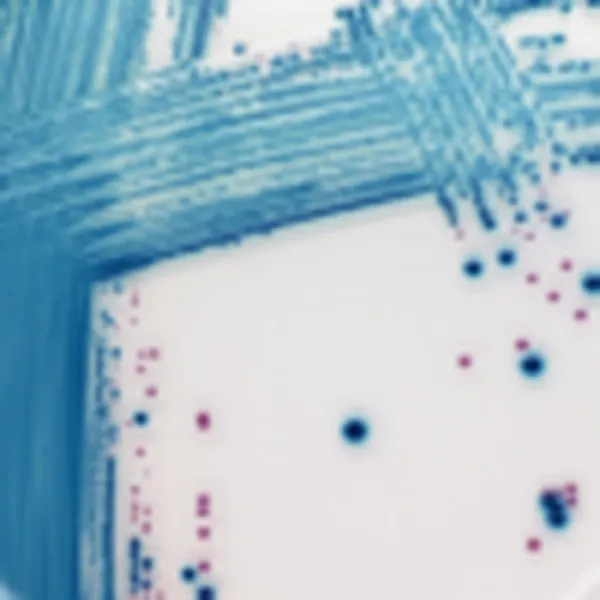
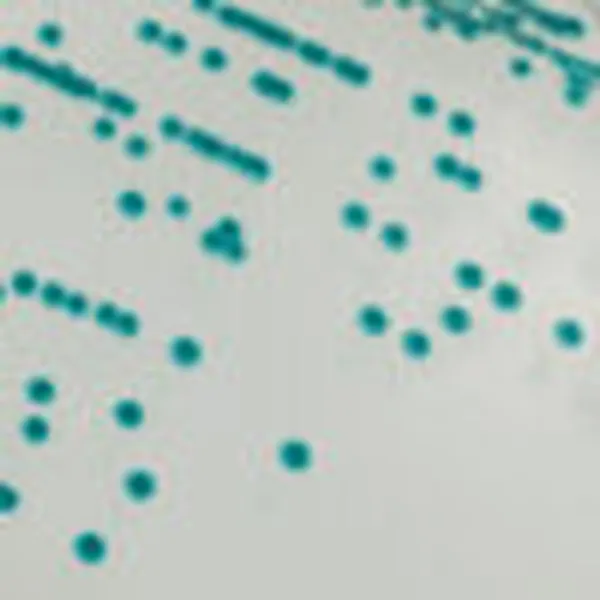
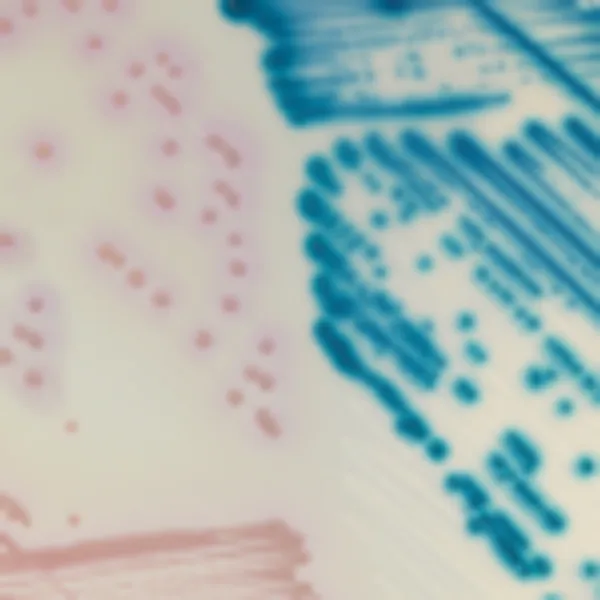
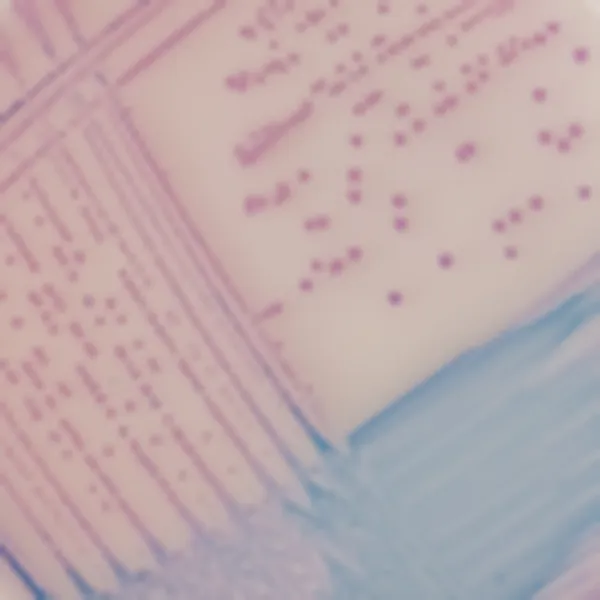
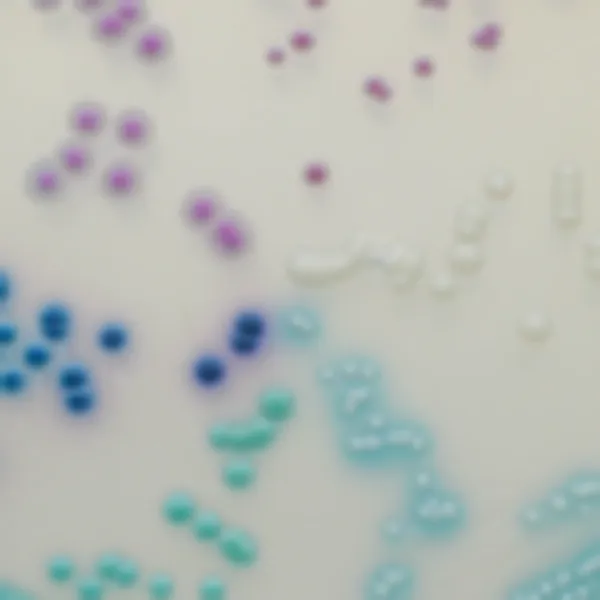
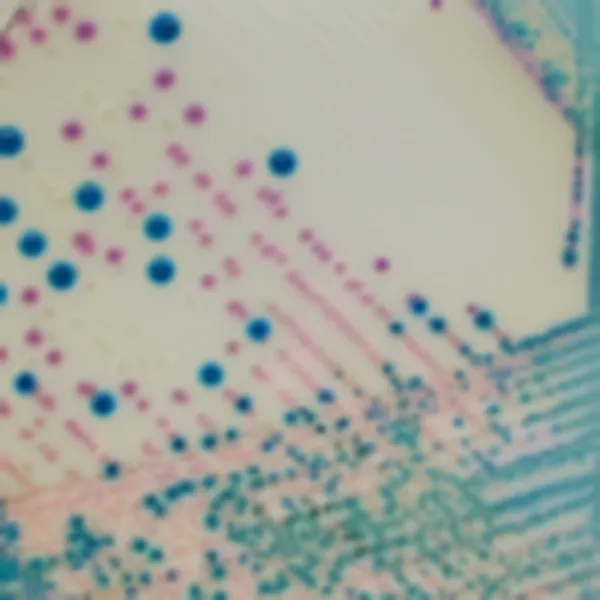
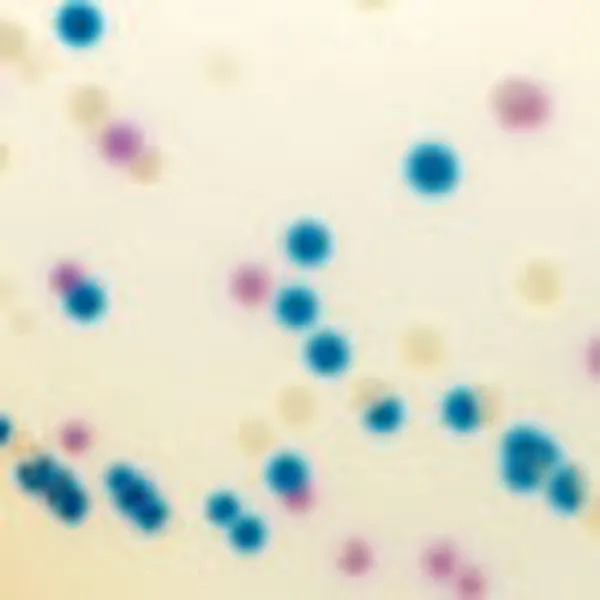
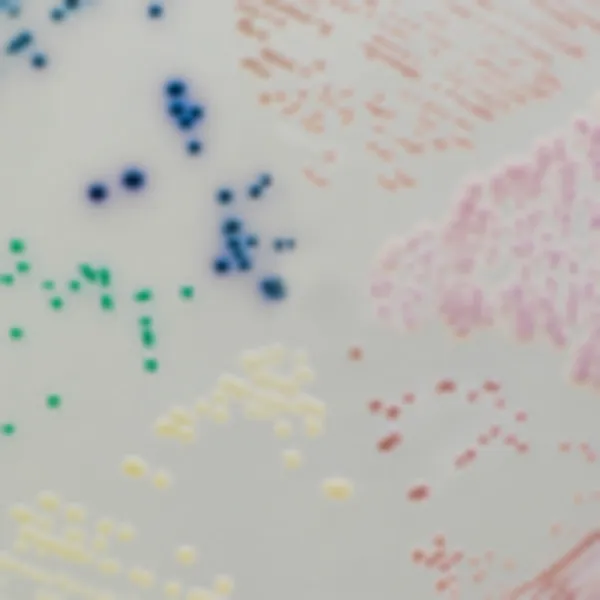
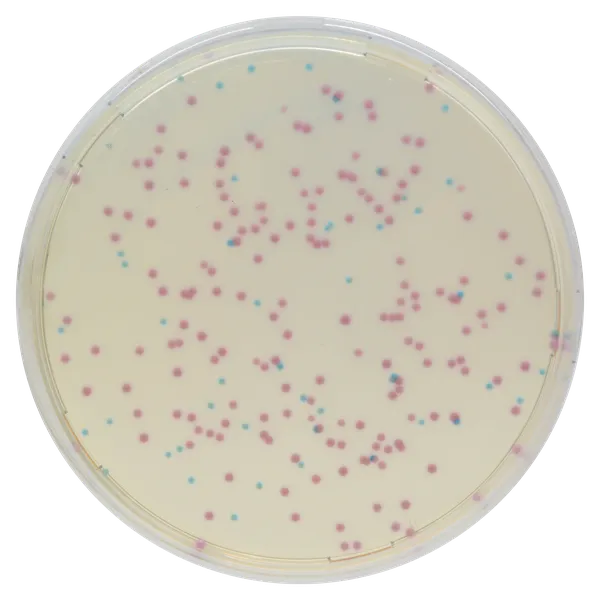
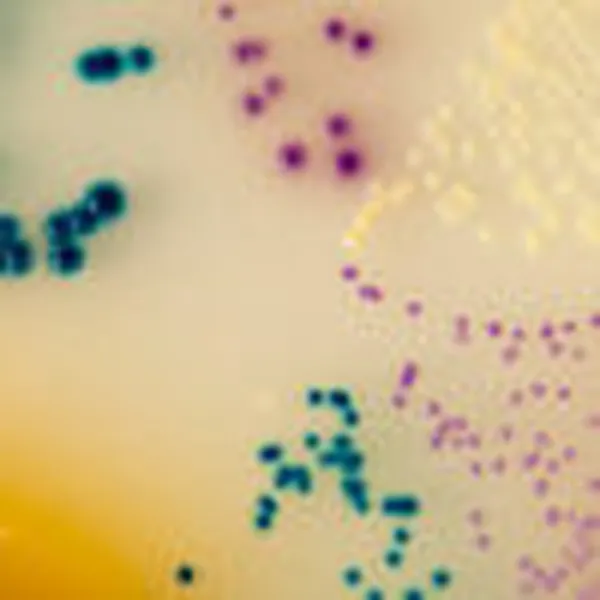
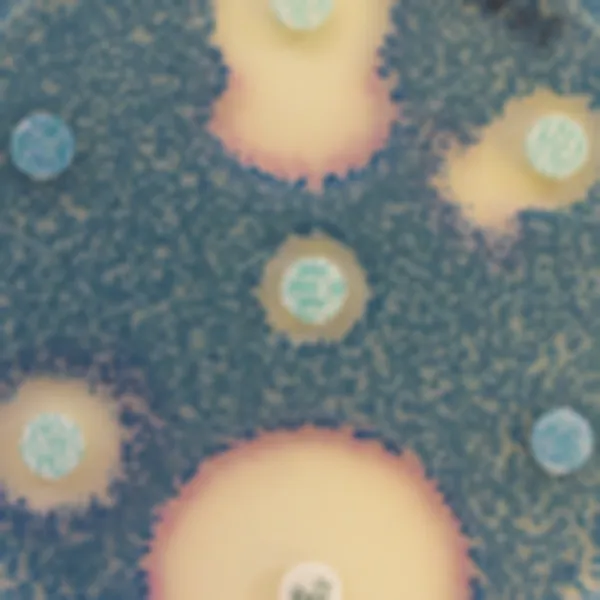
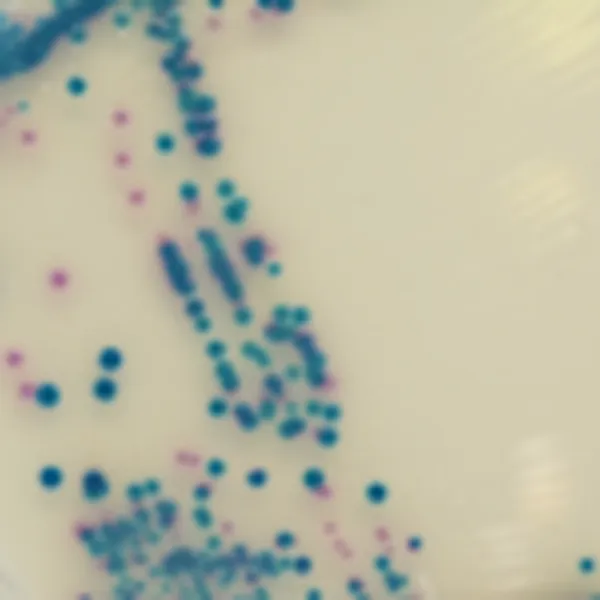
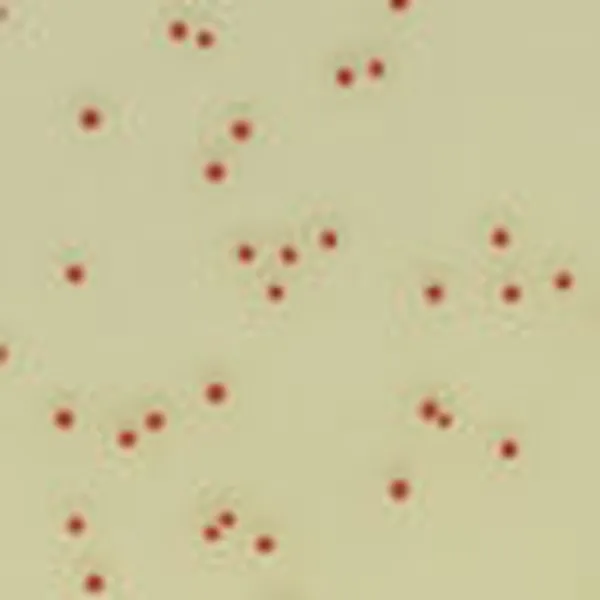
Colonies Appearance
Performance
Performance
Leading cause of nosocomial infections, especially in intensive care units, the MRSA sources are either endogenous (the patient) or through cross contamination (environmental or by person to person contact). The major issue with this pathogen is its resistance to a large panel of antibiotics, among them beta-lactam antibiotics, limiting the therapeutic options for clinicians.
Early detection is essential for controlling the spread of MRSA, providing appropriate care, and avoiding complex and expensive treatments. Pre-admission screening for MRSA has proved to be an effective method for reducing the hospital burden of MRSA-colonised patients. The savings due to consistent decolonisation before elective admission outweigh the costs of screening. Today, in the US, the extra-expenses linked to difficult treatments of MRSA infections are estimated at $2.4 billion for about 370,000 hospital stays. (Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology News, August 2009).
In the UK, the estimation of the additional cost of discharging every hospital patient who acquires MRSA is £9,000.
Intended Use :
CHROMagar™ MRSA is a selective and differential chromogenic medium for the qualitative direct detection of colonization by methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) to aid in the prevention and control of MRSA in healthcare settings. The test is performed on anterior nares or perineal swab specimens from patients and healthcare workers to screen for MRSA colonization. Results can be interpreted after 18-24 h of aerobic incubation at 35-37 °C.
CHROMagar™ MRSA is not intended to diagnose, guide, nor monitor therapy for MRSA infections, nor provide results of susceptibility to methicillin. A lack of growth or the absence of pink colonies on CHROMagar™ MRSA does not preclude the presence of MRSA. Further identification, susceptibility testing, and epidemiological typing is needed on suspect colonies.
CHROMagar™ MRSA can also be used in conjunction with other laboratory tests and clinical data available to aid in the identification and in the diagnosis of MRSA infections in skin, soft tissue, wounds and positive blood cultures. Concomitant cultures are necessary to recover organisms for further microbiological susceptibility testing or epidemiological typing.
1. Absolutely reliable: CHROMagar™ MRSA, introduced in 2002, was the first chromogenic medium for MRSA detection. It lead to such significant reductions in both, the response time and laboratory workload, that it allowed an absolutely necessary wide-scale patient screening.
2. Efficient: The medium exhibits sensitivity and specificity values close to 100 %. CHROMagar™ MRSA allows an accurate detection of MRSA with a higher level of sensitivity than oxacillin containing media.
3. Fast & easy interpretation: Intense mauve colony colour in 18-24 h.

Composition
Technical Documents
Scientific Publications
2023
Methicillin-resistant Staphyloccocus spp. Colonization among pregnant women considering different scenarios related to Covid-19 pandemic in Brazil
📄 Publication2023
Detection of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) by CHROMagar Versus Cefoxitin Disk Diffusion Method
📄 Publication2022
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus spp. colonization among pregnant women considering scenarios before and after the onset of COVID-19 pandemic in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
📄 Publication2022
Multidrug resistant bacteria on air, inanimate surface and medical equipment in an intensive care unit in Lima, Peru
📄 Publication2018
Media Makes a Difference in the Detection of Surveillance Isolates of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus using the Bruker MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry MRSA PSM-mec Detection Module
📄 Publication2017
Implementation of Colorex MRSA/VRE bi-plate on WASP/WASPLab to screen for MRSA and VRE using Eswab duo swab
📄 Publication2016
Evaluation of Different Phenotypic and Genotypic Methods for Detection of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
📄 Publication2015
Screening agars for MRSA: evaluation of a stepwise diagnostic approach with two different selective agars for the screening for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
📄 Publication2014
Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus and Methicillinresistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) from human clinical specimens using conventional biochemical tests and Chromogenic media
📄 Publication2012
Performance of CHROMagar Staph aureus and CHROMagar MRSA for Detection of Airborne Methicillin-Resistant and Methicillin-Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus DOI: 10.1080/02786826.2011.626001
📄 Publication2012
A multi-beach study of Staphycoloccus aureus, MRSA, and enterococci in seawater and beach sand
📄 Publication2011
Evaluation of a new CHROMagar Medium for Detection of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
📄 Publication2006
Evaluation of a new chromogenic medium for isolation and presumptive identification of methicillin-resitant Staphylococcus aureus from human clinical specimens
📄 Publication2005
Performance of CHROMagar MRSA medium for detection of Methicillin-Resitant Staphylococcus aureus.
📄 Publication2005
Evaluation of CHROMagar MRSA for detection of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
📄 Publication2005
Evaluation of new CHROMagar MRSA to detection of MRSA from the clinical specimens. (Heavy file > 6,2 Mbytes)
📄 Publication



















Read more